Available courses
- Teacher: MS.AMUDHA G OBG NURSING
It starts with full dilatation of cervix and ends with expulsion of fetus from birth canal. Duration is 2 hours in primipara and 30 minutes in multipara.
- Teacher: MS.AMUDHA G OBG NURSING
Fertilization is the process of fusion of the spermatozoon with the mature ovum. The fertilization process takes approximately 24 hours.
"Organization
consists of the relationship of individual to individuals and group to groups
which are so related as to bring about an orderly division of labor.“
- Teacher: PROF. JAMUNARANI G OBG NURSING
i) Power orientation
ii)Leadership as a continuum
iii) Likert's management system
iv) Managerial grid
v)Tri dimensional grid
6. Situational theory or Contingency theory
i)Fielder’s contingency model
ii)Hersey and Blanchard’s situational model
- Teacher: PROF. JAMUNARANI G OBG NURSING
- Teacher: PROF. JAMUNARANI G OBG NURSING
Water is one of the natural resources, which are found in an adequate amount. It is an essential source for the existence of life on
- Teacher: E.Manju Asst.prof ICON
Housing in the modern concept includes not
only the physical structure providing shelter,
but also the immediate surrounding and the
related community service and facility it is
defined as the all places in which a group of
people residential and follow their life goals,
the size of the settlement may vary from a
singles family to millions of people.
- Teacher: E.Manju Asst.prof ICON
A chalk board or black board is a reusable writing surface made of wood, ply, hardboard, cement, ground glass, asbestos, slate, plastic etc. with black, green, bluish green.
- Teacher: MS.AMUDHA G OBG NURSING
- Teacher: MS.AMUDHA G OBG NURSING
Standards Psy N
- Teacher: Mrs.Jayanthi Assoc.prof ICON COLLEGE
India became the first country in the world to formulate a National Family Planning Programme in 1952, with the objective of "reducing birth rate to the extent necessary to stabilize the population at a level consistent with requirement of national economy".
- Teacher: E.Manju Asst.prof ICON
- Teacher: E.Manju Asst.prof ICON
- Teacher: E.Manju Asst.prof ICON
- Teacher: E.Manju Asst.prof ICON
Arrhythmia is a heart condition that causes the heart to beat abnormally fast, slow, or irregularly. It can be life-threatening and is treated with lifestyle changes, medications, or medical procedures.
- Teacher: Vice Principal ICON
Pulmonary Edema ; is a condition characterized by fluid accumulation in the lungs caused by extravasation of fluid from pulmonary vasculature in to the interstitium and alveoli of the lungs
- Teacher: Vice Principal ICON
- Teacher: Vice Principal ICON
Gynecomastia is an increase in the amount of breast gland tissue in boys or men, caused by an imbalance of the hormones estrogen and testosterone. Gynecomastia can affect one or both breasts, sometimes unevenly.
Hypospadias is the most common congenital anomaly of the penis. In this anomaly the urethral opening is situated on the ventral side of the shaft of penis in one or several positions, just behind the glans.
Cirrhosis is a chronic progressive disease of the liver characterized by extensive degeneration and destruction of the liver parenchymal cells.
Cirrhosis is a chronic progressive disease of the liver characterized by extensive degeneration and destruction of the liver parenchymal cells.
A brain tumor (or brain tumour) is an intracranial solid neoplasm, a tumor (defined as an abnormal growth of cells) within the brain or the central spinal canal.
- Teacher: Saranya.T ICON
A bone tumor refers to a neoplastic growth of tissue in bone. Abnormal growths found in the bone can be either benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
- Teacher: Saranya.T ICON
Consciousness can be defined as a state of awareness of one's self and the environment, and others, and assessed through set of responses to that environment.
- Teacher: Saranya.T ICON
The
slipped disc is misleading, as an intervertebral disc, being tightly
sandwiched between two vertebrae to which the disc is attached, cannot actually
"slip", "slide", or even get "out of place".
- Teacher: Saranya.T ICON
Skin disorders may be generalized, localized to one or
several sites of abnormality known as ‘lesions, or eruptive, in which case many
lesions appear spottily over the skin.
- Teacher: Saranya.T ICON
- Teacher: Saranya.T ICON
Acute renal failure is a syndrome of varying causation that results in a sudden decline in renal function. It is frequently associated with an increase in BUN and creatinine, oliguria (less than 500 mL urine/24 hours), hyperkalemia, and sodium retention.
- Teacher: Saranya.T ICON
- Teacher: Saranya.T ICON
Spinal cord is considered most important for the body movement since all the nerves exit from the spinal cord. Injury to the spinal cord results in loss of body functions.
- Teacher: Vice Principal ICON
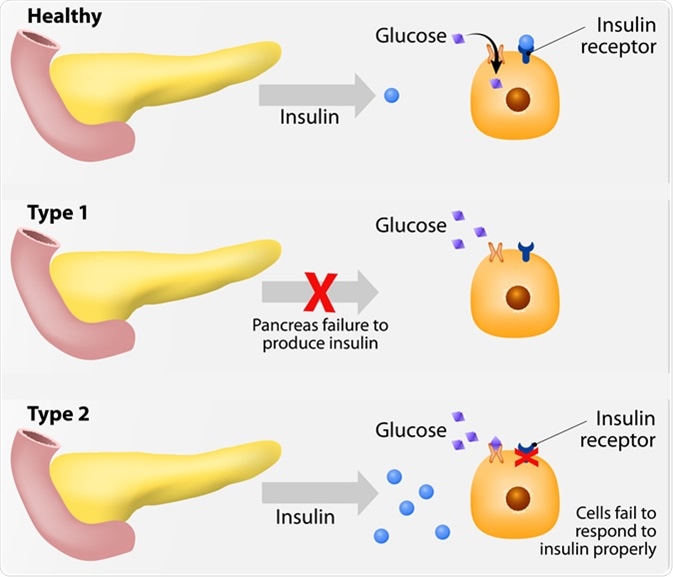
Diabetes is a condition that results from lack of the hormone insulin in a person's blood, or when the body has a problem using the insulin it produces (insulin resistance).
Appendicitis is an infection and inflammation of appendix.
![]()
- Teacher: Saranya.T ICON
This is for III year students - to find the notes of neurological system
http://neurological system
This is for III year students - to find the notes of neurological system.
Instrutor- Prof.Chandndralekha.K
The elderly unit consist of introduction, definition, psychological aspect of elderly, theories, stress management, medication etc.
UNIT- I INTRODUCTION
SPSS (Statistical Package for Social Science) is a Statistical Package for data analysis, it is a very popular software (Paid) because of its friendly usage in Social & Medical Sciences Research Analytics.
Statistics is concerned with scientific method for collecting, organizing, summarizing, presenting ,analysis and interpretation of numerical data as well as drawing valid conclusions and making reasonable decisions on the basis of such analysis
THIS WILL HELP THE STUDENTS TO ACQUIRE KNOWLEDGE ON THE STEPS OF NURSING RESEARCH AND APPLY IN PRACTICAL SETTING.
This course is to create awareness about the true experimental design and develop desirable attitude and skill in the application of this design among the students.
Neonatal resuscitation also known as newborn resuscitation is an emergency procedure focused on supporting the approximately 10% of newborn children who do not readily begin breathing, putting them at risk of irreversible organ injury and death.
Paediatric nursing is the specialized area of the nursing practice concerning the care of children during wellness and illness, which includes preventive, promotive, curative and rehabilitative care of children.
- Teacher: Vijayasri.V ICON
THERAPEUTIC PLAY IS THE SPECIALIZED PLAY ACTIVITY WHICH A CHILD ACTS OUT OR
EXPRESSES HIS UNCONSCIOUS FEEL INGS. IT IS A CENTRAL MECHANISM IN WHICH CHILDREN
COPE, COMMUNICATE, LEARN AND MASTER A TRAUMATIC EXPERIENCE SUCH AS
HOSPITALIZATION. IT IS GUIDED BY HEALTH TEAM MEMBERS
- Teacher: Vijayasri.V ICON
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver. Inflammation is swelling that happens when tissues of the body are injured or infected. It can damage your liver. This swelling and damage can affect how well your liver functions.
Hepatitis can be an acute (short-term) infection or a chronic (long-term) infection. Some types of hepatitis cause only acute infections. Other types can cause both acute and chronic infections.
- Teacher: Vijayasri.V ICON
DS, also called Trisomy 21, is a genetic condition that causes delays in physical and intellectual development. • There is extra genetic material from chromosome 21, so individuals with DS have 47 chromosomes in total instead of the usual 46.
- Teacher: Vijayasri.V ICON
The organization of good quality special care neonatal unit is essential for reducing the neonatal mortality and improving the quality of life among survivors.
- mmediate care at birth (delayed cord clamping, thorough drying, assessment of breathing, skin-to-skin contact, early initiation of breastfeeding)
- Thermal care.
- Resuscitation when needed.
- Support for breast milk feeding.
- Nurturing care.
- Infection prevention.
- Assessment of health problems.
- mmediate care at birth (delayed cord clamping, thorough drying, assessment of breathing, skin-to-skin contact, early initiation of breastfeeding)
- Thermal care.
- Resuscitation when needed.
- Support for breast milk feeding.
- Nurturing care.
- Infection prevention.
- Assessment of health problems.
Kangaroo mother care is a method of care of preterm infants. The method involves infants being carried, usually by the mother, with skin-to-skin contact. This guide is intended for health professionals responsible for the care of low-birth-weight and preterm infants.
- mmediate care at birth (delayed cord clamping, thorough drying, assessment of breathing, skin-to-skin contact, early initiation of breastfeeding)
- Thermal care.
- Resuscitation when needed.
- Support for breast milk feeding.
- Nurturing care.
- Infection prevention.
- Assessment of health problems.
Growth is defined as an irreversible constant increase in size, and development is defined as growth in psychomotor capacity.
The endocrine system
is a network of glands that produce and release hormones that help
control many important body functions, including the body's ability to
change calories into energy that powers cells and organs. The endocrine
system influences how your heart beats, how your bones and tissues grow, even your ability to make a baby. It plays a vital role in whether or not you develop diabetes, thyroid disease, growth disorders, sexual dysfunction, and a host of other hormone-related disorders.
Neonatal Intensive Care is defined as, “care for medically unstable and critically ill newborns requiring constant nursing, complicated surgical procedures, continual respiratory support, or other intensive interventions.”
- Teacher: Lakshmi Priya .N (TUTOR) ICON
Behavioral disorders involve a pattern of disruptive behaviors in children that last for at least 6 months and cause problems in school, at home and in social situations.
- Teacher: Vijayasri.V ICON
DEFINITION:
Essential newborn care involves immediate care at the time of birth, and essential care during the entire newborn period. It is needed both in the health facility and at home.
- Teacher: Lakshmi Priya .N (TUTOR) ICON
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a persistent opening between the two major blood vessels leading from the heart.
TYPES
- Type A = pure
esophageal atresia; type
- B = esophageal atresia with proximal
tracheoesophageal fistula; type
- C = esophageal atresia with distal
tracheoesophageal fistula; type
- D = esophageal atresia with proximal and
distal tracheoesophageal fistula; type
- E = H-type tracheoesophageal
fistula without esophageal atresia
National Health Programmes are launched by the Central Government for the control/ eradication of the communicable diseases, improvement of environmental sanitation, improving the standard of nutrition, control of population and promotion of rural health.
- Teacher: Vijayasri.V ICON
National Health Programmes are launched by the Central Government for the control/ eradication of the communicable diseases, improvement of environmental sanitation, improving the standard of nutrition, control of population and promotion of rural health.
- Teacher: Vijayasri.V ICON
Pediatrics is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, adolescents, and young adults
- Teacher: Vijayasri.V ICON
Monitoring of neonates is the keynote to
their successful outcome.
• Accurate nursing observation is a vital
factor in the survival and future
development of newborn.The initial physical examination should be
performed as soon as after the birth.
• All newborns should be thoroughly
examined in the first 24-48 hrs of age.
Congenital heart disease is a general term for a range of birth defects that affect the normal way the heart works. The term "congenital" means the condition is present from birth. Congenital heart disease is one of the most common types of birth defect, affecting almost 1 in 100 babies
A fracture happens when more force is applied to the bone than the bone can absorb. It can happen from overuse injuries, falls, trauma, or a direct hit to the body. A child with a broken bone may have pain, swelling, and trouble moving the injured area. Treatment may include a cast or splint, pain medicine, or surgery.
- Teacher: Mrs.Rosi.S - Lecturer OBG ICON
Hirschsprung's (HIRSH-sproongz) disease is a condition that affects the large intestine (colon) and causes problems with passing stool.
- Teacher: Mrs.Rosi.S - Lecturer OBG ICON
- Teacher: Vijayasri.V ICON
Kangaroo mother care is a method of care of preterm infants. The method involves infants being carried, usually by the mother, with skin-to-skin contact.
- Teacher: Lakshmi Priya .N (TUTOR) ICON
Common health problems in babies include colds, coughs, fevers, and vomiting. Babies also commonly have skin problems, like diaper rash or cradle cap. Many of these problems are not serious. It is important to know how to help your sick baby, and to know the warning signs for more serious problems.
- Teacher: Lakshmi Priya .N (TUTOR) ICON
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is a combination of four congenital (present at birth) heart defects that affect infants and children.
The defects occur together and change the way blood flows through the
heart and lungs. TOF occurs in about 1 out of every 2,518 babies born in
the U.S. each year.
RHEUMATIC FEVER: A disease that can result from inadequately treated strep throat or scarlet fever.
Overview. A seizure is a sudden, uncontrolled electrical disturbance in the brain. It can cause changes in your behavior, movements or feelings, and in levels of consciousness
A seizure is a sudden, uncontrolled electrical disturbance in the brain. It can cause changes in your behavior, movements or feelings, and in levels of consciousness.
INSTRUCTOR:
MS. VAISHNAVI. L
- Teacher: MS.VAISHNAVI L CHILD HEALTH NURSING
Mrs. CHANDRALEKA.E
![]()
MRS.CHANDRALEKA.E
Course about the Baby Friendly Hospital Initiative
- Teacher: Course Creator 3
Immunization is one of the most cost effective ways to protect and prevent humans from infectious diseases. Immunization is a process of including immunity artificially through the administration of antigenic agents.
Supply of pure uncontaminated safe drinking
water is essential to achieve optimum health. Water-borne diseases are caused
by pathogenic microorganisms that most commonly ute transmitted in contaminated
fresh water. Infection com monly results during bathing washing: drinking in
the preparation of food, or the consumption of food that is infected.
Women Empowerment is the process and the outcome of the process by which women challenge gender based discrimination in every institution and structures of the society.
A
rapid increase in the size of a population caused by such factors as a sudden
decline in infant mortality or an increase in life expectancy.
- Teacher: E.Manju Asst.prof ICON
The
concept of health is defined as "a balanced state of well-being resulting
from harmonious interactions of body, mind, and spirit."
Comprehensive child health care implies assurance of extensive health services for all children, from birth to 18 years of age, for a set of health conditions.
u SBA training is to enhance the knowledge and skills of the ANM’S /LHV posted at the out reach centeres, first referrals units so that they are proficient in the skills needed for.
Ventilation is the intentional introduction of outdoor air into a space. Ventilation is mainly used to control indoor air quality by diluting and displacing indoor pollutants; it can also be used to control indoor temperature, humidity, and air motion to benefit thermal comfort, satisfaction with other aspects of indoor environment, or other objectives.
- Teacher: E.Manju Asst.prof ICON
¡ Survey all the families in his area and collect general information about each village/locality in his area.
Quality antenatal care and monitoring is very essential to diagnose and
treat maternal disorders that pre-exist or develop during pregnancy
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation within the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is perceived by the human eye.
- Teacher: E.Manju Asst.prof ICON
Population policy in general refers to policies intended to the reduce birth rate or growth rate. In April 1976, India formed its first national population policy. In 1977, it was modified. National population policy 2000 is the latest in this series.
All
human activities produce waste. We all know that such waste may be dangerous
and needs safe disposal. Industrial waste, sewage and agricultural waste
pollute water, soil and air. It can also be dangerous to human beings and
environment. Similarly, hospitals and other health care facilities generate lots
of waste which can transmit infections, particularly HIV, Hepatitis B & C
and Tetanus, to the people who handle it or come in contact with it
Vital Health
Statistics' is defined as 'the facts, systemically collected and compiled in
numerical form, related to or derived from records of vital events'. These
vital events are births, deaths, marriages, illnesses of a particular community
![]() Health care
delivery system refers to the totality of resources that a population or
Health care
delivery system refers to the totality of resources that a population or
society distributes in the organisation and delivery of health population services. Italso includes all personal and public services performed by individuals orinstitutions for the purpose of maintaining or restoring health.
COMMUNITY
COMMUNITY MEANS THE GROUP OF PEOPLE LIVING TOGETHER IN A PARTICULAR GEOGRAPHICAL AREAS.
RUBELLA
MUMPS
EPIDEMIOLOGY
THEY ARE THE LIFE THREATENING MEDICAL CONDITIONS THAT OCCUR IN PREGNANCY,DURING OR AFTER LABOUR.
- Teacher: MS.AMUDHA G OBG NURSING
The amniotic fluid that bathes the fetus is necessary for its proper growth and development. It cushions the fetus from physical trauma, permits fetal lung growth, and provides a barrier against infection. Normal amniotic fluid volume varies..
- Teacher: MS.AMUDHA G OBG NURSING
MIDWIFE:
“A midwife is a person who having been regularly admitted to a midwifery educational program fully recognized in the country in which it is located has successfully completed the prescribed course of studies in midwifery and has acquired the requisite qualifications to be registered and or legally licensed to practise midwifery“
-International confideration of Midwives, 1972
Excessive blood loss after giving birth—known as obstetric hemorrhage and shock—is the leading cause of maternal death worldwide.
- Teacher: Mrs.Rosi.S - Lecturer OBG ICON
UNIT - III IMPORTANT QUESTIONS AND ANSWER
The pelvis is the area of the body below the abdomen that is located between the hip bones and contains the bladder and rectum.
- Teacher: Mrs.Rosi.S - Lecturer OBG ICON
Postnatal exercises are started to mother who has recently given birth. We have to give stretches and strengthening.
- Teacher: MS.AMUDHA G OBG NURSING
INSTRUCTOR NAME: PROF.JAMUNARANI.G
INSTRUCTOR NAME: PROF.JAMUNARANI.G
INSRTUCTOR NAME: PROF.JAMUNARANI.G
INSTRUCTOR NAME: PROF.JAMUNARANI.G
INSTRUCTOR NAME: PROF.JAMUNARANI.G
Puerperium is the period following childbirth during which the body tissues, especially the pelvic organs revert back approximately to the pre pregnant state both anatomically and physiologically.
- Teacher: MS.AMUDHA G OBG NURSING
INSTUCTURE NAME: PROF. JAMUNARANI.G
Midwifery is the health science and health profession that deals with pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period (including care of the newborn), in addition to the sexual and reproductive health of women throughout their lives.
- Teacher: Mrs.Rosi.S - Lecturer OBG ICON
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is a virus that attacks the body's immune system. If HIV is not treated, it can lead to AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). There is currently no effective cure. Once people get HIV, they have it for life.
- Teacher: Mrs.Rosi.S - Lecturer OBG ICON
INSTRUCTOR NAME: PROF.JAMUNARANI.G
INSTRUCTOR NAME : PROF.JAMUNARANI.G
A surgical planned incision on the perineum and the posterior vaginal wall during the second stage of labor is called episiotomy (perineotomy).
- Teacher: MS.AMUDHA G OBG NURSING
The puerperium is the period of about 6 weeks, when we give special attention to the changes occurring in the mother's body. These changes primarily include the return of the maternal organs to around pre-pregnant sizes and functions, endocrine changes as the placenta is lost, and the onset of lactation.
- Teacher: Mrs.Rosi.S - Lecturer OBG ICON
INSTRUCTOR NAME: JAMUNARANI.G
- Teacher: Mrs.Jayanthi Assoc.prof ICON COLLEGE
- Teacher: Mrs.Jayanthi Assoc.prof ICON COLLEGE